OkHttp原理解析
基于 OkHttp 3.10.0 版本分析
一、OkHttp介绍
OkHttp是当下Android使用最频繁的网络请求框架,由Square公司开源。
核心优点:
- 支持Http1.X、Http2、WebSocket、QUIC等协议
- 连接池复用底层TCP连接,减少请求延时
- 无缝支持GZIP压缩,减少数据流量
- 缓存响应数据,减少重复请求
- 请求失败自动重试和重定向
二、基本使用
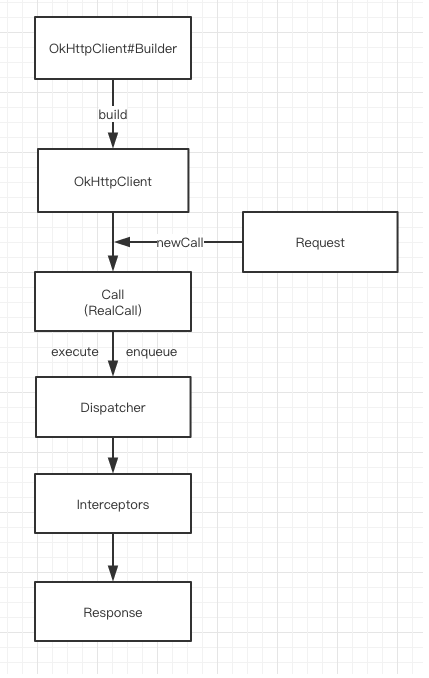
2.1 简单示例
// 1. 创建OkHttpClient
OkHttpClient client = new OkHttpClient.Builder()
.connectTimeout(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
.readTimeout(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
.build();
// 2. 创建Request
Request request = new Request.Builder()
.url("https://api.example.com/data")
.build();
// 3. 同步请求
Response response = client.newCall(request).execute();
// 4. 异步请求
client.newCall(request).enqueue(new Callback() {
@Override
public void onFailure(Call call, IOException e) {
// 请求失败
}
@Override
public void onResponse(Call call, Response response) throws IOException {
// 请求成功
String result = response.body().string();
}
});
2.2 核心概念
- OkHttpClient: 客户端配置,包含连接池、拦截器、超时等配置
- Request: 请求对象,包含URL、请求头、请求体等信息
- Call: 请求的执行者(
RealCall实现),可执行同步或异步请求 - Response: 响应对象,包含响应码、响应头、响应体等信息
三、任务分发器 Dispatcher
Dispatcher 负责调配请求任务,内部维护线程池和请求队列。
3.1 核心参数
// 异步请求同时存在的最大请求数
private int maxRequests = 64;
// 异步请求同一域名同时存在的最大请求数
private int maxRequestsPerHost = 5;
// 异步请求使用的线程池
private ExecutorService executorService;
// 异步等待队列
private final Deque<AsyncCall> readyAsyncCalls = new ArrayDeque<>();
// 异步执行队列
private final Deque<AsyncCall> runningAsyncCalls = new ArrayDeque<>();
// 同步执行队列
private final Deque<RealCall> runningSyncCalls = new ArrayDeque<>();
3.2 同步请求
synchronized void executed(RealCall call) {
runningSyncCalls.add(call);
}
同步请求不需要线程池,仅做记录。
3.3 异步请求
synchronized void enqueue(AsyncCall call) {
// 未超过最大限制64 && 同一Host请求不超过5个
if (runningAsyncCalls.size() < maxRequests && runningCallsForHost(call) < maxRequestsPerHost) {
runningAsyncCalls.add(call);
executorService().execute(call);
} else {
readyAsyncCalls.add(call); // 加入等待队列
}
}
3.4 线程池配置
public synchronized ExecutorService executorService() {
if (executorService == null) {
executorService = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
0, // 核心线程数
Integer.MAX_VALUE, // 最大线程数
60, // 空闲线程存活时间
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>(), // 无容量队列,最大吞吐量
Util.threadFactory("OkHttp Dispatcher", false)
);
}
return executorService;
}
线程池特点:
- 核心线程为0,所有线程60s无工作就回收
- 最大线程数为
Integer.MAX_VALUE,配合SynchronousQueue实现最大吞吐 - 但有最大64个并发请求的限制,避免线程过多
四、拦截器责任链
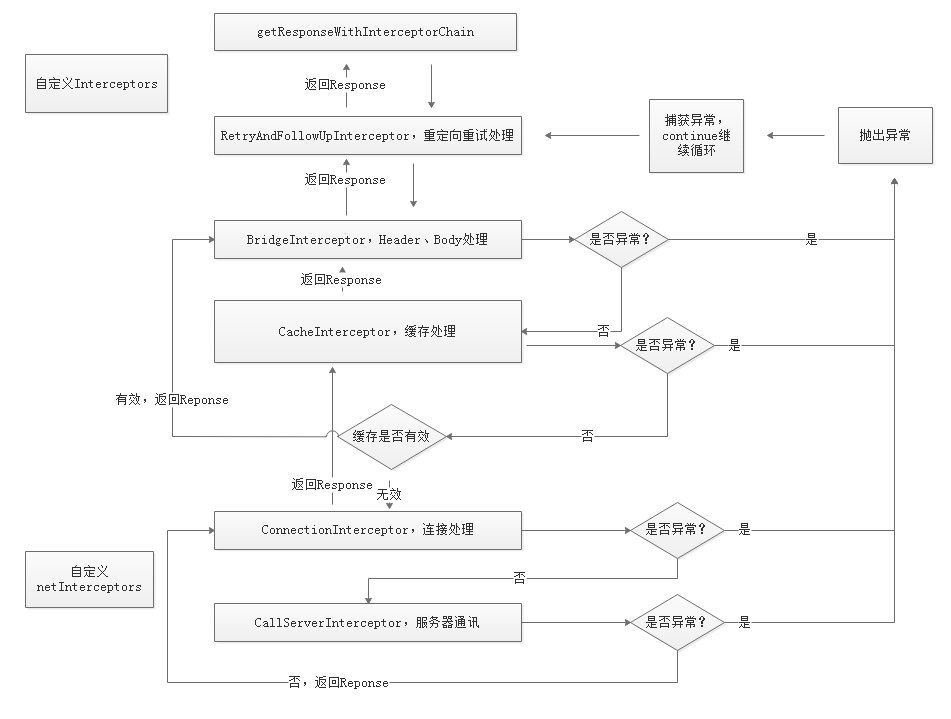
OkHttp 的核心工作机制是责任链模式,请求依次经过五大拦截器处理:
- RetryAndFollowUpInterceptor - 重试与重定向
- BridgeInterceptor - 桥接拦截器,补全请求头
- CacheInterceptor - 缓存拦截器
- ConnectInterceptor - 连接拦截器
- CallServerInterceptor - 请求服务器拦截器
4.1 重试与重定向拦截器
职责: 判断是否需要重试或重定向
重试条件
出现 RouteException 或 IOException 时判断是否重试:
private boolean recover(IOException e, StreamAllocation streamAllocation,
boolean requestSendStarted, Request userRequest) {
// 1. 配置不允许重试
if (!client.retryOnConnectionFailure()) return false;
// 2. 判断是否属于可重试的异常
if (!isRecoverable(e, requestSendStarted)) return false;
// 3. 是否有更多路由线路
if (!streamAllocation.hasMoreRoutes()) return false;
return true;
}
可重试的异常:
- ✅ Socket超时异常
- ❌ 协议异常(请求或响应格式错误)
- ❌ SSL证书异常
重定向
根据响应码判断是否需要重定向:
- 307/308: 临时/永久重定向(仅GET/HEAD)
- 300/301/302/303: 多种重定向状态码
- 401: 需要身份验证,添加
Authorization头 - 407: 需要代理认证,添加
Proxy-Authorization头 - 408: 请求超时,可重试
- 503: 服务不可用,根据
Retry-After决定
注意: 重定向最多20次。
4.2 桥接拦截器
职责: 补全请求头,处理响应
补全的请求头
| 请求头 | 说明 |
|---|---|
Content-Type |
请求体类型 |
Content-Length |
请求体长度 |
Host |
请求的主机站点 |
Connection: Keep-Alive |
保持长连接 |
Accept-Encoding: gzip |
接受gzip压缩 |
Cookie |
Cookie信息 |
User-Agent |
用户代理信息 |
主要工作
- 补全请求头信息
- 保存Cookie(需自定义
CookieJar) - 解压GZIP响应体
4.3 缓存拦截器
职责: 管理HTTP缓存
缓存策略
通过 CacheStrategy 判断,有四种组合:
| networkRequest | cacheResponse | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| Null | Not Null | 直接使用缓存 |
| Not Null | Null | 发起网络请求 |
| Null | Null | 返回504错误 |
| Not Null | Not Null | 发起请求,304则使用缓存 |
关键响应头
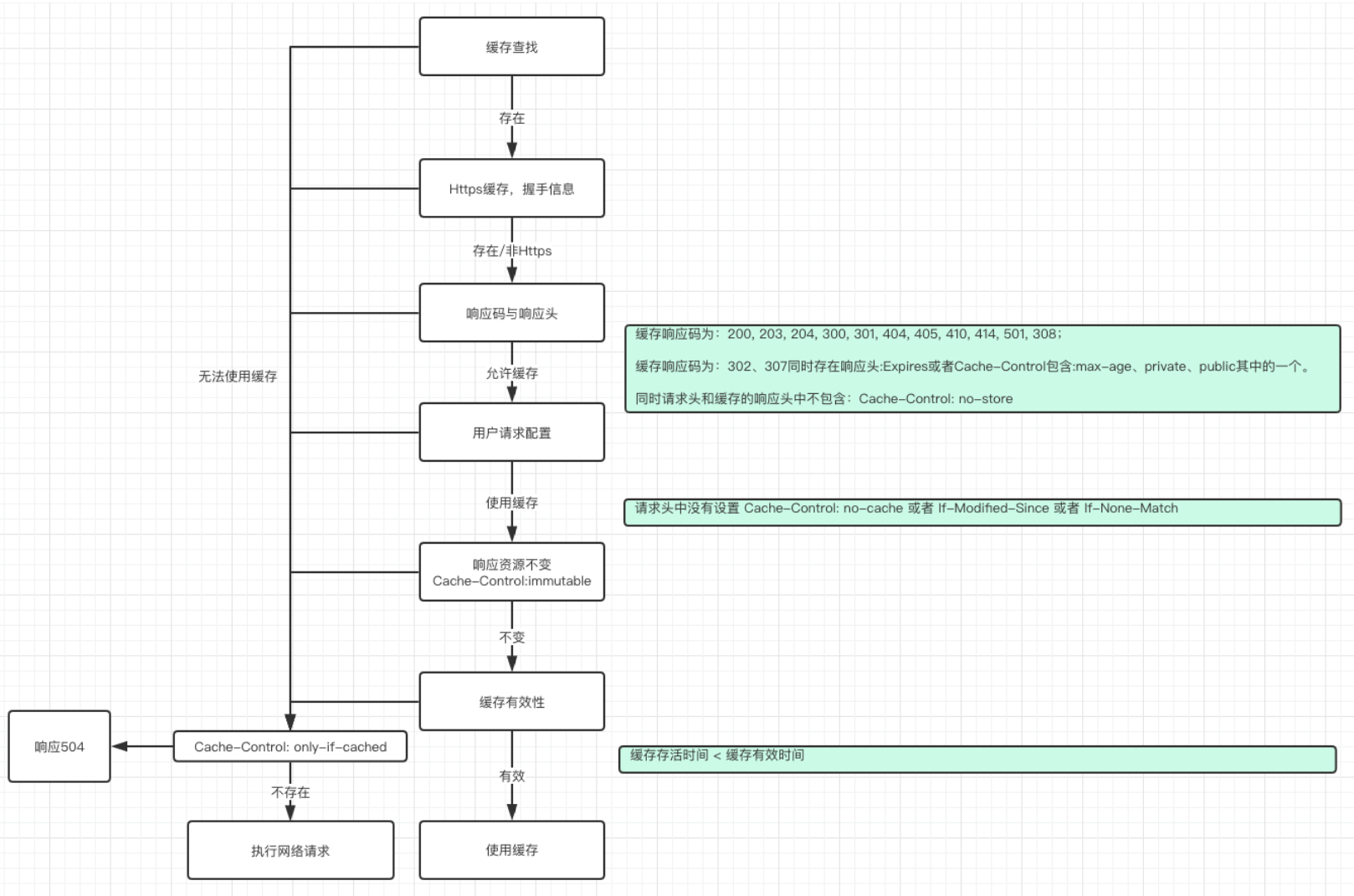
Cache-Control: max-age=3600- 缓存有效期Cache-Control: no-cache- 不使用缓存Cache-Control: no-store- 不存储缓存Etag- 资源唯一标识Last-Modified- 资源最后修改时间
缓存判断流程
// 缓存有效性判断
if (缓存存活时间 + 最小新鲜度 < 缓存有效时长 + 过期后可用时长) {
// 可以使用缓存
return new CacheStrategy(null, cacheResponse);
}
// 缓存过期,发起条件请求
if (etag != null) {
request.header("If-None-Match", etag); // 服务器返回304则使用缓存
} else if (lastModified != null) {
request.header("If-Modified-Since", lastModified);
}
4.4 连接拦截器
职责: 建立与服务器的连接
@Override
public Response intercept(Chain chain) throws IOException {
StreamAllocation streamAllocation = realChain.streamAllocation();
// 获取连接和数据流
HttpCodec httpCodec = streamAllocation.newStream(client, chain, doExtensiveHealthChecks);
RealConnection connection = streamAllocation.connection();
return realChain.proceed(request, streamAllocation, httpCodec, connection);
}
连接复用条件
- 连接未达到最大并发流限制
- DNS、代理、SSL证书、域名、端口完全相同
- 连接未被关闭
4.5 请求服务器拦截器
职责: 发送请求,接收响应
// 1. 写入请求头
httpCodec.writeRequestHeaders(request);
// 2. 写入请求体
if (request.body() != null) {
BufferedSink bufferedSink = Okio.buffer(httpCodec.createRequestBody(request, contentLength));
request.body().writeTo(bufferedSink);
bufferedSink.close();
}
// 3. 完成请求
httpCodec.finishRequest();
// 4. 读取响应头
Response response = httpCodec.readResponseHeaders(false);
// 5. 读取响应体
response = response.newBuilder()
.body(httpCodec.openResponseBody(response))
.build();
Expect: 100-continue 处理:
- 发送请求体前先询问服务器是否接受
- 服务器返回100则继续发送,否则不发送请求体
五、总结
5.1 整体流程
- 用户发起请求 →
Dispatcher分发 - 重试拦截器 → 判断重试/重定向
- 桥接拦截器 → 补全请求头
- 缓存拦截器 → 判断是否使用缓存
- 连接拦截器 → 建立连接(复用连接池)
- 请求拦截器 → 发送请求、接收响应
- 逆序返回 → 各拦截器处理响应
- 返回用户 → 得到最终响应
5.2 核心设计模式
- 建造者模式:
OkHttpClient.Builder、Request.Builder - 工厂模式:
Call的创建 - 责任链模式: 拦截器链
- 享元模式: 连接池复用连接
5.3 关键特性
- 连接池: 复用TCP连接,减少握手开销
- 多路复用: HTTP/2支持单连接多请求
- 自动重试: 智能判断可重试场景
- 缓存管理: 符合HTTP缓存规范
- GZIP压缩: 自动压缩解压
六、高级用法
6.1 自定义拦截器
public class LoggingInterceptor implements Interceptor {
@Override
public Response intercept(Chain chain) throws IOException {
Request request = chain.request();
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
Log.d("OkHttp", "发送请求: " + request.url());
Response response = chain.proceed(request);
long endTime = System.nanoTime();
Log.d("OkHttp", "接收响应: " + response.code() +
", 耗时: " + (endTime - startTime) / 1e6 + "ms");
return response;
}
}
// 应用拦截器
OkHttpClient client = new OkHttpClient.Builder()
.addInterceptor(new LoggingInterceptor()) // 应用拦截器
.addNetworkInterceptor(new LoggingInterceptor()) // 网络拦截器
.build();
区别:
- 应用拦截器: 只调用一次,不关心重定向和重试
- 网络拦截器: 每次网络请求都调用,可以监听实际网络操作
6.2 连接池配置
ConnectionPool connectionPool = new ConnectionPool(
5, // 最大空闲连接数
5, // 连接存活时间
TimeUnit.MINUTES
);
OkHttpClient client = new OkHttpClient.Builder()
.connectionPool(connectionPool)
.build();
6.3 超时配置
OkHttpClient client = new OkHttpClient.Builder()
.connectTimeout(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS) // 连接超时
.readTimeout(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS) // 读取超时
.writeTimeout(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS) // 写入超时
.callTimeout(30, TimeUnit.SECONDS) // 整个请求超时
.build();
6.4 缓存配置
// 创建缓存目录
File cacheDirectory = new File(getCacheDir(), "http_cache");
Cache cache = new Cache(cacheDirectory, 10 * 1024 * 1024); // 10MB
OkHttpClient client = new OkHttpClient.Builder()
.cache(cache)
.build();
// 强制使用缓存
Request request = new Request.Builder()
.url("https://api.example.com/data")
.cacheControl(new CacheControl.Builder()
.onlyIfCached() // 只使用缓存
.maxStale(7, TimeUnit.DAYS) // 缓存过期后7天内仍可用
.build())
.build();
6.5 代理配置
// HTTP代理
Proxy proxy = new Proxy(Proxy.Type.HTTP,
new InetSocketAddress("proxy.example.com", 8080));
// 代理认证
Authenticator proxyAuthenticator = new Authenticator() {
@Override
public Request authenticate(Route route, Response response) throws IOException {
if (response.code() == 407) {
String credential = Credentials.basic("username", "password");
return response.request().newBuilder()
.header("Proxy-Authorization", credential)
.build();
}
return null;
}
};
OkHttpClient client = new OkHttpClient.Builder()
.proxy(proxy)
.proxyAuthenticator(proxyAuthenticator)
.build();
6.6 EventListener 监听请求各阶段
EventListener 可以监听请求的各个阶段,用于统计和调试:
public class CustomEventListener extends EventListener {
private long callStartTime;
@Override
public void callStart(Call call) {
callStartTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Log.d("OkHttp", "请求开始: " + call.request().url());
}
@Override
public void dnsStart(Call call, String domainName) {
Log.d("OkHttp", "DNS解析开始: " + domainName);
}
@Override
public void dnsEnd(Call call, String domainName, List<InetAddress> inetAddressList) {
Log.d("OkHttp", "DNS解析结束: " + domainName + ", IP数量: " + inetAddressList.size());
}
@Override
public void connectStart(Call call, InetSocketAddress inetSocketAddress, Proxy proxy) {
Log.d("OkHttp", "连接开始: " + inetSocketAddress);
}
@Override
public void connectEnd(Call call, InetSocketAddress inetSocketAddress, Proxy proxy, Protocol protocol) {
Log.d("OkHttp", "连接结束,协议: " + protocol);
}
@Override
public void requestHeadersStart(Call call) {
Log.d("OkHttp", "发送请求头开始");
}
@Override
public void requestHeadersEnd(Call call, Request request) {
Log.d("OkHttp", "发送请求头结束");
}
@Override
public void requestBodyStart(Call call) {
Log.d("OkHttp", "发送请求体开始");
}
@Override
public void requestBodyEnd(Call call, long byteCount) {
Log.d("OkHttp", "发送请求体结束,字节数: " + byteCount);
}
@Override
public void responseHeadersStart(Call call) {
Log.d("OkHttp", "接收响应头开始");
}
@Override
public void responseHeadersEnd(Call call, Response response) {
Log.d("OkHttp", "接收响应头结束,状态码: " + response.code());
}
@Override
public void responseBodyStart(Call call) {
Log.d("OkHttp", "接收响应体开始");
}
@Override
public void responseBodyEnd(Call call, long byteCount) {
Log.d("OkHttp", "接收响应体结束,字节数: " + byteCount);
}
@Override
public void callEnd(Call call) {
long duration = System.currentTimeMillis() - callStartTime;
Log.d("OkHttp", "请求结束,总耗时: " + duration + "ms");
}
@Override
public void callFailed(Call call, IOException ioe) {
long duration = System.currentTimeMillis() - callStartTime;
Log.e("OkHttp", "请求失败,耗时: " + duration + "ms", ioe);
}
}
// 使用EventListener
OkHttpClient client = new OkHttpClient.Builder()
.eventListener(new CustomEventListener())
// 如果需要为每个请求创建新的Listener实例
.eventListenerFactory(new EventListener.Factory() {
@Override
public EventListener create(Call call) {
return new CustomEventListener();
}
})
.build();
6.7 上传下载进度监听
下载进度监听
// 自定义ResponseBody包装类
public class ProgressResponseBody extends ResponseBody {
private ResponseBody responseBody;
private ProgressListener progressListener;
private BufferedSource bufferedSource;
public ProgressResponseBody(ResponseBody responseBody, ProgressListener progressListener) {
this.responseBody = responseBody;
this.progressListener = progressListener;
}
@Override
public MediaType contentType() {
return responseBody.contentType();
}
@Override
public long contentLength() {
return responseBody.contentLength();
}
@Override
public BufferedSource source() {
if (bufferedSource == null) {
bufferedSource = Okio.buffer(source(responseBody.source()));
}
return bufferedSource;
}
private Source source(Source source) {
return new ForwardingSource(source) {
long totalBytesRead = 0L;
@Override
public long read(Buffer sink, long byteCount) throws IOException {
long bytesRead = super.read(sink, byteCount);
totalBytesRead += bytesRead != -1 ? bytesRead : 0;
if (progressListener != null) {
progressListener.onProgress(totalBytesRead, responseBody.contentLength(), bytesRead == -1);
}
return bytesRead;
}
};
}
}
// 进度监听接口
public interface ProgressListener {
void onProgress(long bytesRead, long contentLength, boolean done);
}
// 下载拦截器
public class DownloadProgressInterceptor implements Interceptor {
private ProgressListener listener;
public DownloadProgressInterceptor(ProgressListener listener) {
this.listener = listener;
}
@Override
public Response intercept(Chain chain) throws IOException {
Response originalResponse = chain.proceed(chain.request());
return originalResponse.newBuilder()
.body(new ProgressResponseBody(originalResponse.body(), listener))
.build();
}
}
// 使用下载进度监听
OkHttpClient client = new OkHttpClient.Builder()
.addNetworkInterceptor(new DownloadProgressInterceptor(new ProgressListener() {
@Override
public void onProgress(long bytesRead, long contentLength, boolean done) {
int progress = (int) ((100 * bytesRead) / contentLength);
Log.d("Download", "下载进度: " + progress + "%");
// 更新UI
runOnUiThread(() -> {
progressBar.setProgress(progress);
});
}
}))
.build();
上传进度监听
// 自定义RequestBody包装类
public class ProgressRequestBody extends RequestBody {
private RequestBody requestBody;
private ProgressListener progressListener;
public ProgressRequestBody(RequestBody requestBody, ProgressListener progressListener) {
this.requestBody = requestBody;
this.progressListener = progressListener;
}
@Override
public MediaType contentType() {
return requestBody.contentType();
}
@Override
public long contentLength() throws IOException {
return requestBody.contentLength();
}
@Override
public void writeTo(BufferedSink sink) throws IOException {
BufferedSink bufferedSink = Okio.buffer(sink(sink));
requestBody.writeTo(bufferedSink);
bufferedSink.flush();
}
private Sink sink(Sink sink) {
return new ForwardingSink(sink) {
long bytesWritten = 0L;
long contentLength = 0L;
@Override
public void write(Buffer source, long byteCount) throws IOException {
super.write(source, byteCount);
if (contentLength == 0) {
contentLength = contentLength();
}
bytesWritten += byteCount;
if (progressListener != null) {
progressListener.onProgress(bytesWritten, contentLength, bytesWritten == contentLength);
}
}
};
}
}
// 使用上传进度监听
File file = new File("/path/to/file");
RequestBody requestBody = RequestBody.create(MediaType.parse("application/octet-stream"), file);
RequestBody progressRequestBody = new ProgressRequestBody(requestBody, new ProgressListener() {
@Override
public void onProgress(long bytesWritten, long contentLength, boolean done) {
int progress = (int) ((100 * bytesWritten) / contentLength);
Log.d("Upload", "上传进度: " + progress + "%");
// 更新UI
runOnUiThread(() -> {
progressBar.setProgress(progress);
});
}
});
Request request = new Request.Builder()
.url("https://api.example.com/upload")
.post(progressRequestBody)
.build();
