思想
存储:
- 找一个存放入度为零这些点的东西,队列,表都可以。
- 一个链表存放点,也就是邻接表。
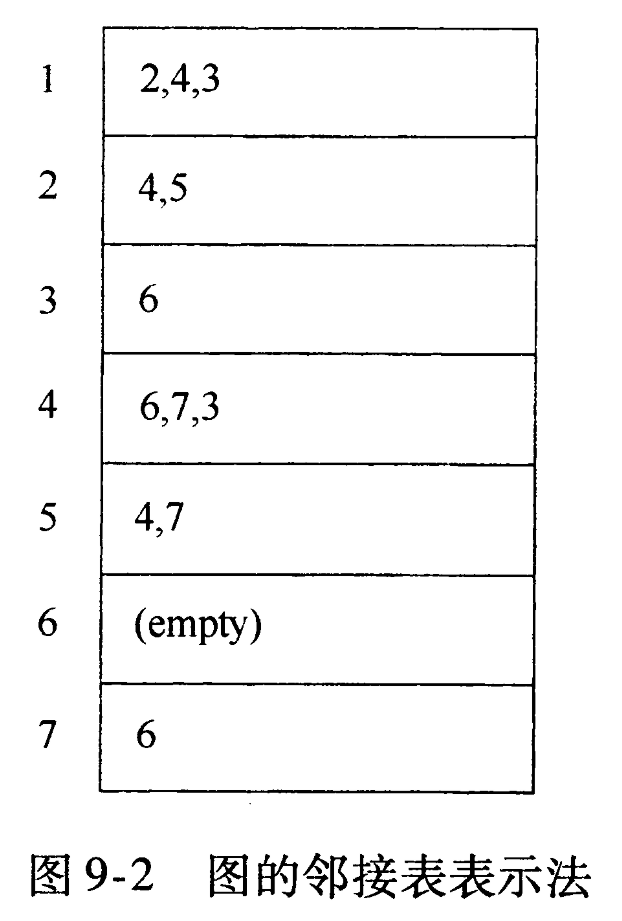
- 首先,对每个顶点计算它的入度。
- 然后,将所有人度为0的顶点放人一个初始为空的队列中。
- 当队列不空时,删除一个顶点v,并将 与v邻接的所有顶点的入度均减1。
- 只要一个顶点的入度降为0,就把该顶点放人队列中。此 时,拓扑排序就是顶点岀队的顺序。
步骤
- 定义存放入度为零的顶点的队列
- 把邻接矩阵换位邻接表
- 定义出队顺序编号变量
- 先找一遍所有入度为零的点,放到队列
- 循环出队,安排出队序号,指向的点入度减一。如果队列空,没有入度为0的,有环
- 如果序号最大值不等于点数,有环
代码
public class Graph {
/**
* 把邻接矩阵转邻接表
*
* @param matrix 图的邻接矩阵,点从0开始
*/
private static List<Vertex<Integer>> adjMatrix2List(Integer[][] matrix) {
//1. 定义点的列表,要初始化好入度,指向的点,值
List<Vertex<Integer>> vertexList = new LinkedList<>();
//2. 遍历每一个点,找其所有adjVertex
for (int i = 0; i < matrix.length; i++) {
Integer[] edges = matrix[i];
Vertex<Integer> vertex = new Vertex<>(i);
for (int j = 0; j < edges.length; j++) {
//点有指向这个j点
if (edges[j] == 1) {
vertex.nextVertices.add(j);
}
}
vertexList.add(vertex);
}
//3. 统计每个点入度
for (int i = 0; i < matrix.length; i++) {
int indegree = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < matrix.length; j++) {
//对每一列遍历
if (matrix[j][i] == 1) {
indegree++;
}
}
//对每个点设置入度
vertexList.get(i).indegree = indegree;
}
return vertexList;
}
/**
* 标准拓扑排序
*
* @param matrix 图的邻接矩阵,点从0开始.
* @throws CycleFoundException 有环
*/
public static List<Vertex<Integer>> topSort(Integer[][] matrix) throws CycleFoundException {
//1. 定义存放入度为零的顶点的队列
Queue<Vertex<Integer>> vertexQueue = new LinkedList<>();
//2.把邻接矩阵换位邻接表
List<Vertex<Integer>> vertexList = adjMatrix2List(matrix);
//3. 定义出队的顺序编号
int counter = 0;
//4. 找所有入度为零的点
for (Vertex<Integer> vertex : vertexList) {
if (vertex.indegree == 0) {
vertexQueue.add(vertex);
}
}
//5. 出队,安排出队序号,指向的点入度减一。如果队列空,没有入度为0的,有环
while (!vertexQueue.isEmpty()) {
//1. 出队,假如随机出来就可以有不同排列
Vertex<Integer> v = vertexQueue.poll();
System.out.println("v" + (v.value + 1));
//2. 指定排序序号数字
v.topNum = ++counter;
//3. v出队之后,对每个v指向的点,入度减一。如果减为零,入队
for (Integer x :
v.nextVertices) {
// 找x对应的点
for (Vertex<Integer> vertex : vertexList) {
if (x.equals(vertex.value)) {
// 入度减一,为零则进队
if (--vertex.indegree == 0) {
vertexQueue.add(vertex);
}
break;
}
}
}
}
//6. 如果序号最大值不等于点数,有环
if (counter != vertexList.size()) {
throw new CycleFoundException();
}
return vertexList;
}
static class CycleFoundException extends Exception {
}
private static class Vertex<AnyType extends Comparable<? super AnyType>> {
AnyType value;
int topNum;//出队时排第几
int indegree;
LinkedList<AnyType> nextVertices;
public Vertex(AnyType value) {
this.value = value;
this.topNum = 0;
this.indegree = 0;
this.nextVertices = new LinkedList<>();
}
}
}
测试代码

public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer[][] m = {
{0,1,1,1,0,0,0,},
{0,0,0,1,1,0,0,},
{0,0,0,0,0,1,0,},
{0,0,1,0,0,1,1,},
{0,0,0,1,0,0,1,},
{0,0,0,0,0,0,0,},
{0,0,0,0,0,1,0,},
};
try {
Graph.topSort(m);
} catch (Graph.CycleFoundException e) {
System.err.println("发现环");
}
}
}
输出
v1, v2, v5, v4, v3, v7, v6,
